Doctors in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) have issued an alarm after 15 people d!ed from one of the world’s most de@dly diseases.
Officials are making rapid efforts to prevent the spread of Ebola, which first appeared in the southern part of the country last month.
There have been 28 cases discovered thus far, and four medical staff have already lost their lives.
The virus has now spread throughout the DRC sixteen times.

One of the most dangerous viruses in the world is Ebola
The African nation’s health ministry stated that when a 34-year-old pregnant woman was taken to the hospital in the Kasai district with a high fever and vomiting, officials were alerted to the latest outbreak.
We don’t know if this woman has perished since then.

According to Mohamed Janabi, the World Health Organization’s (WHO) regional director for Africa, the UN agency was “acting with determination to quickly stop the spread of the virus and protect communities.”
The WHO has sent experts to the area to collaborate with a quick reaction team from the DRC to help improve health institutions’ ability to prevent, identify, treat, and control diseases.
Janabi, on the other hand, said that “case numbers are likely to rise as transmission continues.”
The official stated that response teams and local teams will work together to discover persons who may be infected and need care so that everyone may be safe as soon as possible.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the DRC possesses 2,000 doses of the Ervebo vaccine and a supply of medications.
People who have the virus and healthcare personnel on the front lines should get such things in Kasai.
A consignment of medical supplies and mobile lab equipment will also be dispatched.
During the last outbreak in the DRC three years ago, six individuals perished.
But during another outbreak from 2018 to 2020, almost 2,300 people d!ed.
How dangerous is Ebola?
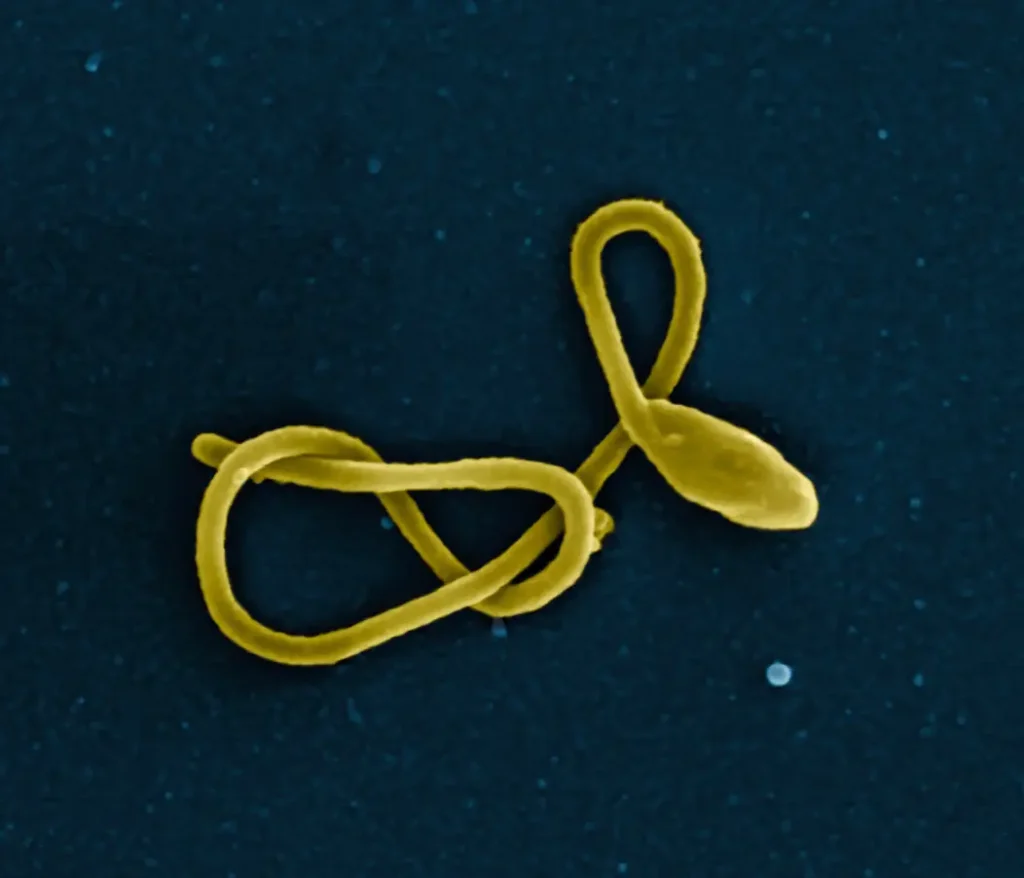
Ebola is a viral hemorrhagic illness that gets its name from a river in the DRC.
The disease was found in 1976, and it is one of the de@dliest on Earth, killing more than half of those who have it—53.6 percent, to be exact.
It spreads through contact with bodily fluids, and the main signs include diarrhea, fever, vomiting, and bleeding.
It can be very hard to stop outbreaks in places where there are a lot of people, especially in cities where there are a lot of buildings.
Some creatures, such bats, monkeys, and porcupines, get sick naturally. People can get sick by eating uncooked “bushmeat.”

People who are infected don’t spread the disease until two to three weeks after they get it, and only after they show symptoms.
There were 11 occurrences in the US in 2014, and four of them were confirmed by a lab.
Two of the people perished in the end.
None of the people who d!ed got the disease in the United States. Most of the cases were people who were medically evacuated from other nations.
